Adaptive Adversarial Training to Improve Adversarial Robustness of DNNs for Medical Image Segmentation and Detection
Paper and Code
Jun 02, 2022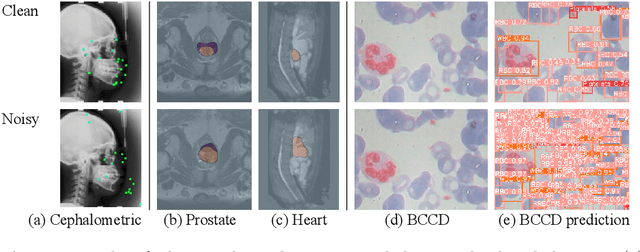
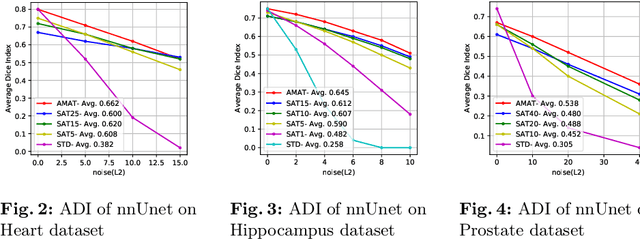
Recent methods based on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) have reached high accuracy for medical image analysis, including the three basic tasks: segmentation, landmark detection, and object detection. It is known that DNNs are vulnerable to adversarial attacks, and the adversarial robustness of DNNs could be improved by adding adversarial noises to training data (i.e., adversarial training). In this study, we show that the standard adversarial training (SAT) method has a severe issue that limits its practical use: it generates a fixed level of noise for DNN training, and it is difficult for the user to choose an appropriate noise level, because a high noise level may lead to a large reduction in model performance, and a low noise level may have little effect. To resolve this issue, we have designed a novel adaptive-margin adversarial training (AMAT) method that generates adaptive adversarial noises for DNN training, which are dynamically tailored for each individual training sample. We have applied our AMAT method to state-of-the-art DNNs for the three basic tasks, using five publicly available datasets. The experimental results demonstrate that our AMAT method outperforms the SAT method in adversarial robustness on noisy data and prediction accuracy on clean data. Please contact the author for the source code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge