A Semi-Markov Chain Approach to Modeling Respiratory Patterns Prior to Extubation in Preterm Infants
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2018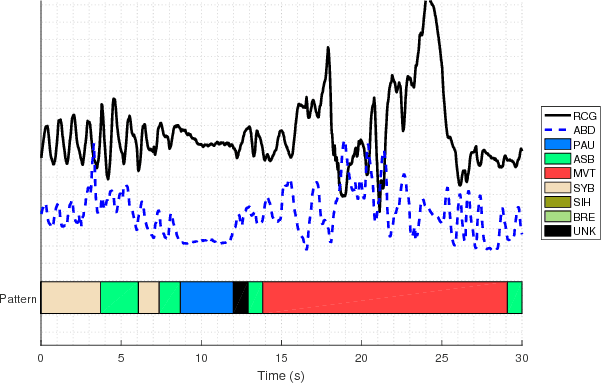
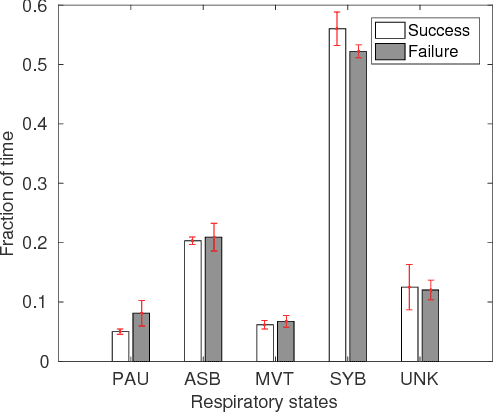
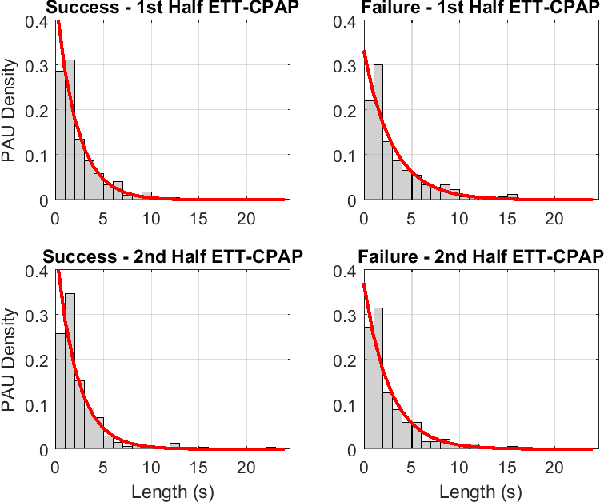
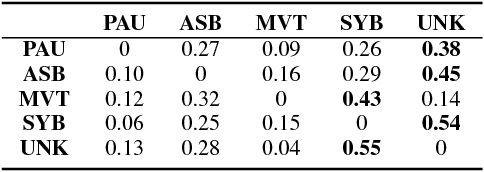
After birth, extremely preterm infants often require specialized respiratory management in the form of invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV). Protracted IMV is associated with detrimental outcomes and morbidities. Premature extubation, on the other hand, would necessitate reintubation which is risky, technically challenging and could further lead to lung injury or disease. We present an approach to modeling respiratory patterns of infants who succeeded extubation and those who required reintubation which relies on Markov models. We compare the use of traditional Markov chains to semi-Markov models which emphasize cross-pattern transitions and timing information, and to multi-chain Markov models which can concisely represent non-stationarity in respiratory behavior over time. The models we developed expose specific, unique similarities as well as vital differences between the two populations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge