A New Weighted Time Window-based Method to Detect B-point in ICG
Paper and Code
Jul 10, 2022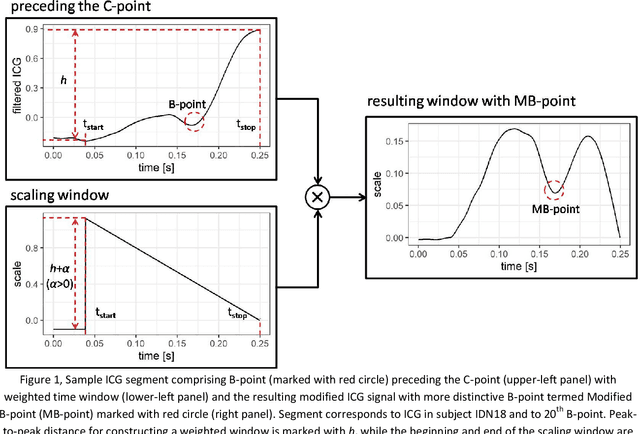
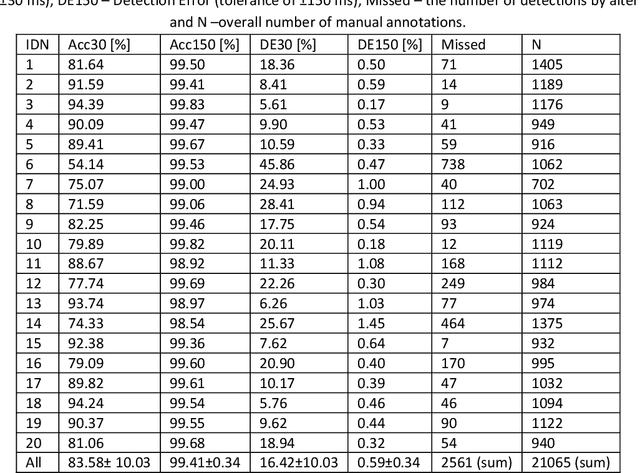
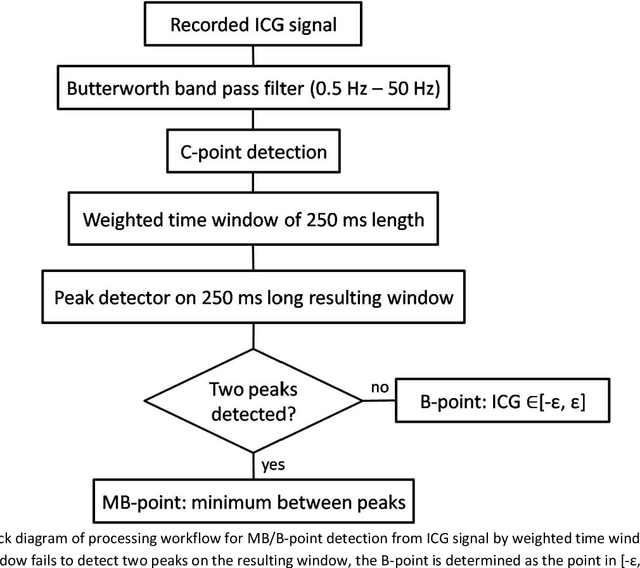
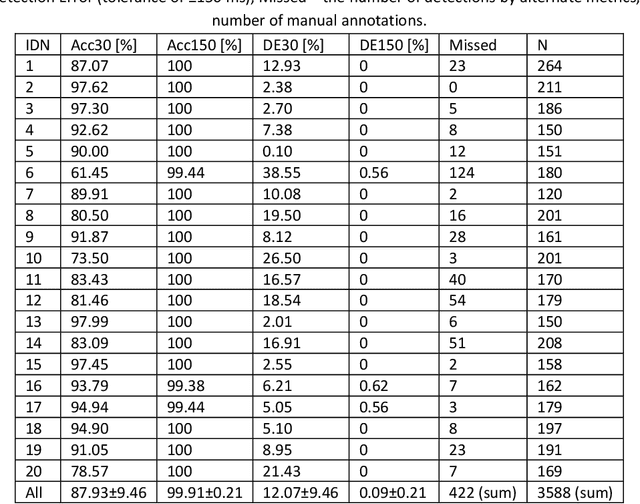
Background and Objectives: A simple, adaptive, and efficient method to detect the beginning of the left ventricular ejection in Impedance Cardiogram (ICG) or the so-called B-point is presented. From implementation perspective this method is designed in time domain and could be exploited for real-time implementation. Methods: The core of the new method is transformation by weighted time window of an ICG segment preceding the maximal ICG peak (the C-point) aiming at the B-point enhancement. The resulting Modified B-point (MB-point) is then easily delineated. To evaluate the proposed workflow for B-point detection based solely on ICG signal, the dataset comprising 20 healthy participants and 21065 B-points are manually annotated and openly shared with the software code. To the best of our knowledge, this is the largest reported and shared ICG dataset for delineation. Detector performance was evaluated on two recorded segments with less and more distinct noises, as well as on an available dataset from the internet comprising ICG recorded in another set of 24 healthy subjects. Results: The results showed that the method was superior when the tolerance for B-point detection was set to +/-150 ms in all cases and for both datasets (>99.4%). Conclusions: In conclusion, proposed approach based on the weighted time windows presents a promising technique for reliable ICG delineation and even for further customization for labeling of other biomedical signals such as electrocardiogram and photopletismogram.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge