A modified Genetic Algorithm for continuous estimation of CPR quality parameters from wrist-worn inertial sensor data
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2019

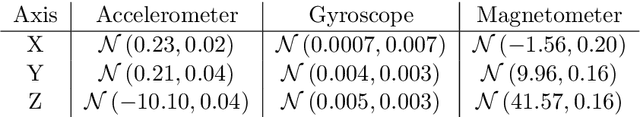

Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is the most important emergency intervention for sudden cardiac arrest. In this paper, a robust sinusoidal model fitting method based on a modified Genetic Algorithm for CPR quality parameters - naming chest compression frequency and depth - as measured by an inertial sensor placed at the wrist is presented. Once included into a smartphone or smartwatch app, the proposed algorithm will enable bystanders to improve CPR (as part of a continuous closed-loop support-system). By evaluating the precision of the model with both, simulated data and data recorded by a Laerdal Resusci Anne mannequin as reference standard, a variance for compression frequency of +-3.7 cpm has been found for the sensor placed at the wrist. Thereby, this previously unconsidered position and consequently the use of smartwatches was shown to be a suitable alternative to the typical placement of phones in the hand for CPR training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge