A machine learning approach to investigate regulatory control circuits in bacterial metabolic pathways
Paper and Code
Jan 13, 2020
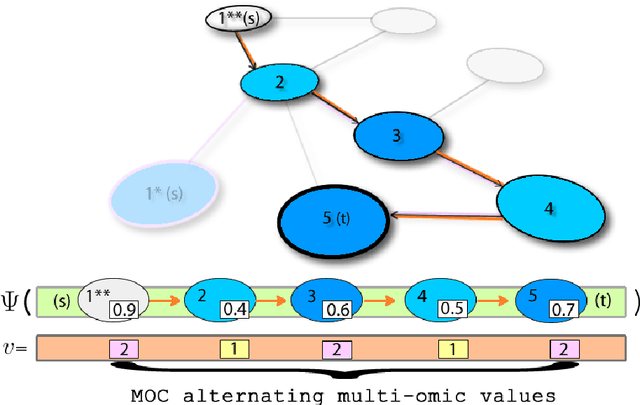

In this work, a machine learning approach for identifying the multi-omics metabolic regulatory control circuits inside the pathways is described. Therefore, the identification of bacterial metabolic pathways that are more regulated than others in term of their multi-omics follows from the analysis of these circuits . This is a consequence of the alternation of the omic values of codon usage and protein abundance along with the circuits. In this work, the E.Coli's Glycolysis and its multi-omic circuit features are shown as an example.
* CIBB 2016 13th International Meeting, CIBB 2016, Stirling, UK,
September 1-3, 2016, Revised Selected Papers Springer, 2017, Vol. 10477 pp
22-26 * 5 pages, 3 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge