A general-purpose method for applying Explainable AI for Anomaly Detection
Paper and Code
Jul 23, 2022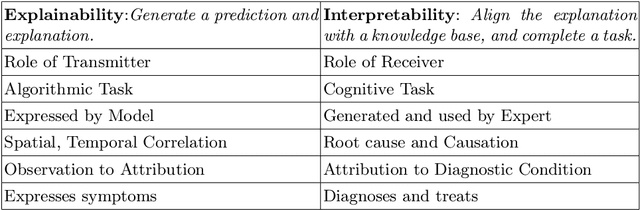
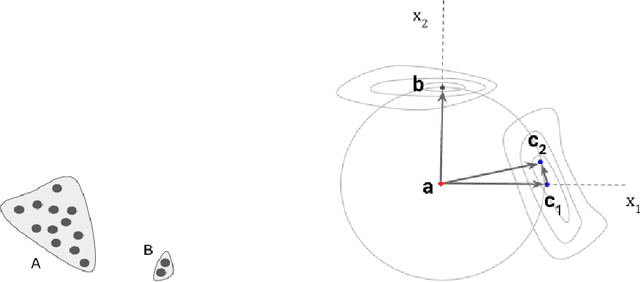

The need for explainable AI (XAI) is well established but relatively little has been published outside of the supervised learning paradigm. This paper focuses on a principled approach to applying explainability and interpretability to the task of unsupervised anomaly detection. We argue that explainability is principally an algorithmic task and interpretability is principally a cognitive task, and draw on insights from the cognitive sciences to propose a general-purpose method for practical diagnosis using explained anomalies. We define Attribution Error, and demonstrate, using real-world labeled datasets, that our method based on Integrated Gradients (IG) yields significantly lower attribution errors than alternative methods.
* 26th International Symposium on Intelligent Systems (ISMIS 2022)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge