A Computational Model for Situated Task Learning with Interactive Instruction
Paper and Code
Apr 23, 2016
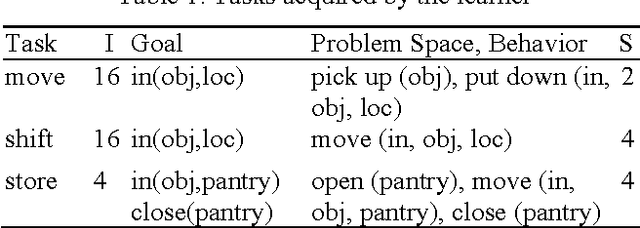


Learning novel tasks is a complex cognitive activity requiring the learner to acquire diverse declarative and procedural knowledge. Prior ACT-R models of acquiring task knowledge from instruction focused on learning procedural knowledge from declarative instructions encoded in semantic memory. In this paper, we identify the requirements for designing compu- tational models that learn task knowledge from situated task- oriented interactions with an expert and then describe and evaluate a model of learning from situated interactive instruc- tion that is implemented in the Soar cognitive architecture.
* International Conference on Cognitive Modeling, 2013
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge