A comparative analysis of preamble sequences for Galvanic Coupling Intra-Body Communications
Paper and Code
Jul 01, 2024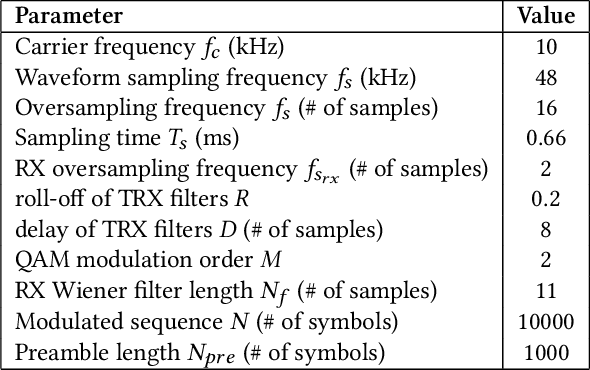
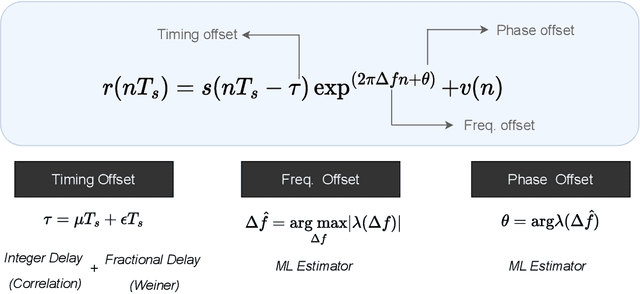
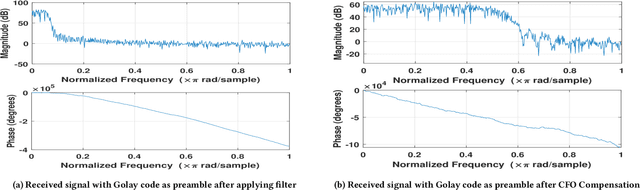
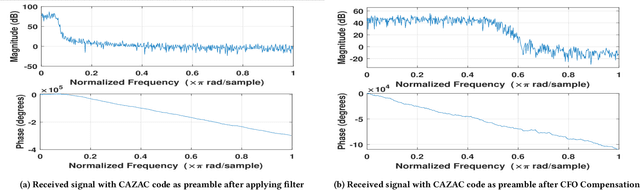
Galvanic coupled-intra-body communication (GC-IBC) is an innovative research area contributing to transform personalized medicine by enabling seamless connectivity and communication among implanted devices. To establish a reliable communication link between implanted devices, the preambles play a crucial role by e.g. conveying syncronization information or supporting channel response estimation. The preambles are carefully designed to ensure that they are mutually orthogonal, to minimize self-interference and maximize separability. For that purpose, many permeable sequences are proposed in the literature for 5G and sensor networks. Golay code, Constant Amplitude Zero Auto Correlation (CAZAC) and Zadoff-Chu (Z-Chu) sequences are among the most popular ones. In this work, we performed a comparative analysis of these sequences to determine their suitability for the GC-IBC system. We evaluated the effectiveness of the preamble sequences on the basis of their correlation properties and probability of error.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge