A Comparative Analysis of Distributional Term Representations for Author Profiling in Social Media
Paper and Code
May 21, 2019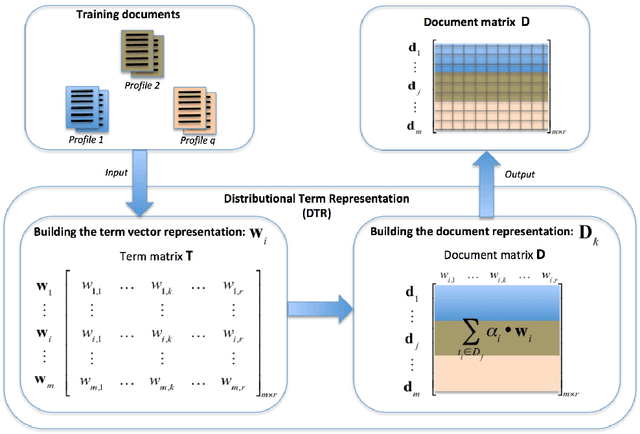
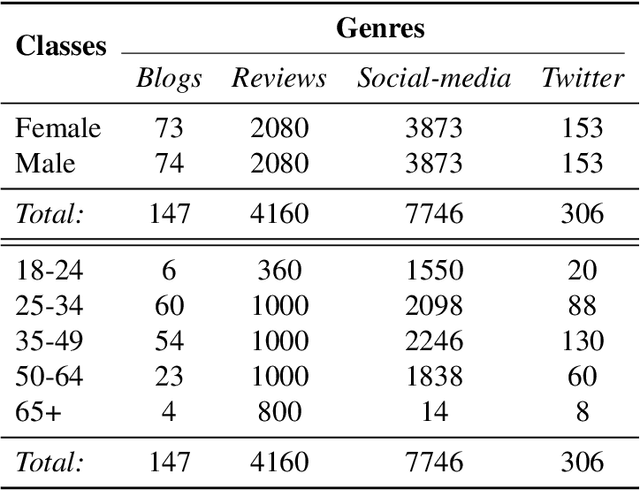
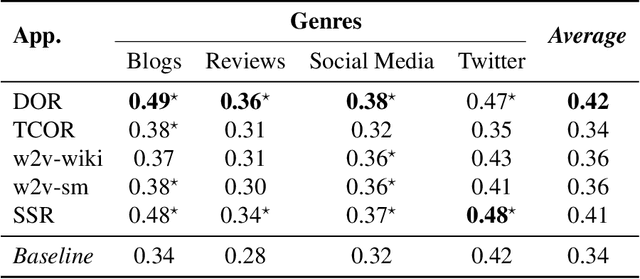
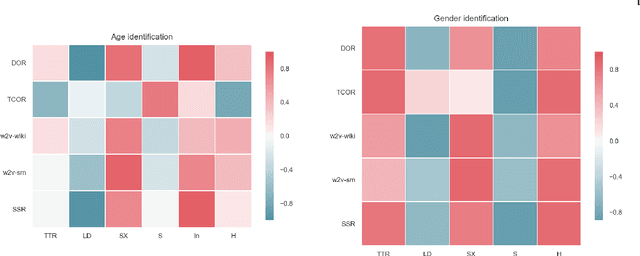
Author Profiling (AP) aims at predicting specific characteristics from a group of authors by analyzing their written documents. Many research has been focused on determining suitable features for modeling writing patterns from authors. Reported results indicate that content-based features continue to be the most relevant and discriminant features for solving this task. Thus, in this paper, we present a thorough analysis regarding the appropriateness of different distributional term representations (DTR) for the AP task. In this regard, we introduce a novel framework for supervised AP using these representations and, supported on it. We approach a comparative analysis of representations such as DOR, TCOR, SSR, and word2vec in the AP problem. We also compare the performance of the DTRs against classic approaches including popular topic-based methods. The obtained results indicate that DTRs are suitable for solving the AP task in social media domains as they achieve competitive results while providing meaningful interpretability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge