A circular microphone array with virtual microphones based on acoustics-informed neural networks
Paper and Code
Feb 24, 2024
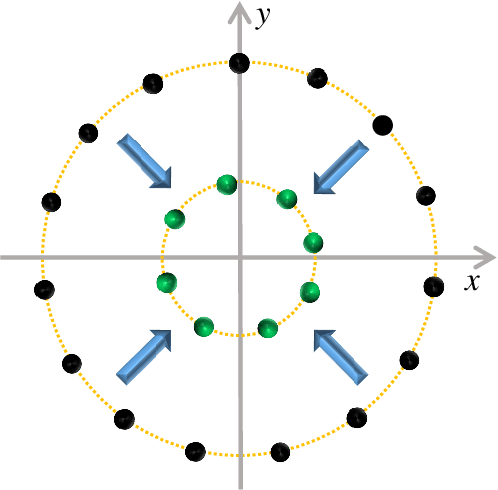
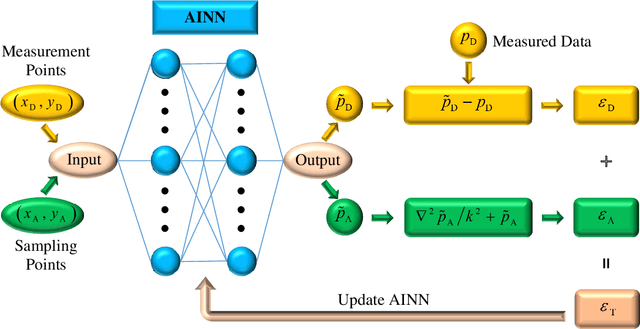
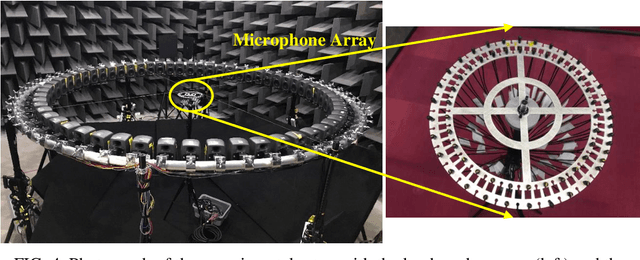
Acoustic beamforming aims to focus acoustic signals to a specific direction and suppress undesirable interferences from other directions. Despite its flexibility and steerability, beamforming with circular microphone arrays suffers from significant performance degradation at frequencies corresponding to zeros of the Bessel functions. To conquer this constraint, baffled or concentric circular microphone arrays have been studied; however, the former needs a bulky baffle that interferes with the original sound field whereas the latter requires more microphones that increase the complexity and cost, both of which are undesirable in practical applications. To tackle this challenge, this paper proposes a circular microphone array equipped with virtual microphones, which resolves the performance degradation commonly associated with circular microphone arrays without resorting to physical modifications. The sound pressures at the virtual microphones are predicted from those measured by the physical microphones based on an acoustics-informed neural network, and then the sound pressures measured by the physical microphones and those predicted at the virtual microphones are integrated to design the beamformer. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach not only eliminates the performance degradation but also suppresses spatial aliasing at high frequencies, thereby underscoring its promising potential.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge